Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
和田 有希*; 鴨川 仁*; 久保 守*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 林 省吾*; 澤野 達也*; 米徳 大輔*; 土屋 晴文
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 128(21), p.e2023JD039354_1 - e2023JD039354_20, 2023/11
被引用回数:0During the 2020-2021 winter season, we detected 6 gamma-ray glows at Kanazawa University, Japan. Negative surface electric fields (E-fields) were observed by a field mill during all the glow cases. In five of the six cases, the maximum E-field reached  12
12 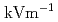 , and the E-field during the glow detection was the strongest in 3 hours before and after the detection time. Therefore, negative charges should have been dominant in the thunderclouds that produced the gamma-ray glows, and electrons were probably accelerated and multiplied by the E-fields between a predominantly negative charge layer and a localized positive charge layer below. In addition, we extracted 8 non-detection cases in the 2020-2021 winter season, in which surface E-fields were stronger than
, and the E-field during the glow detection was the strongest in 3 hours before and after the detection time. Therefore, negative charges should have been dominant in the thunderclouds that produced the gamma-ray glows, and electrons were probably accelerated and multiplied by the E-fields between a predominantly negative charge layer and a localized positive charge layer below. In addition, we extracted 8 non-detection cases in the 2020-2021 winter season, in which surface E-fields were stronger than  12
12 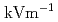 . In 5 of the 8 cases, radar echoes were inadequately developed, suggesting insufficient charge accumulation. On the other hand, the remaining 3 cases had well-developed radar echoes, and there was no significant difference from the detection cases.
. In 5 of the 8 cases, radar echoes were inadequately developed, suggesting insufficient charge accumulation. On the other hand, the remaining 3 cases had well-developed radar echoes, and there was no significant difference from the detection cases.
和田 有希*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中澤 知洋*; 森本 健志*; 中村 佳敬*; 篠田 太郎*; 土屋 晴文
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 128(15), p.e2023JD038606_1 - e2023JD038606_9, 2023/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:58.15(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)A gamma-ray glow, a minute-lasting burst of high-energy photons from a thundercloud, was detected by ground-based apparatus at Kanazawa University, Japan, in a winter thunderstorm on 18 December 2018. The gamma-ray glow was quenched by a lightning flash within a brief time window of 40 ms. The lightning flash produced several low-frequency (LF) E-change pulses that were temporally coincident withthe termination of the gamma-ray glow, and that were located within 0.5 km from the observation site by the Fast Antenna Lightning Mapping Array. The LF pulses had the same polarity as a positive cloud-to-ground current and a normal-polarity in-cloud current. Since this polarity is against the upward electric field for producing the gamma-ray glow (accelerating electrons to the ground), we infer that the glow was terminated by a normal-polarity in-cloud discharge activity between a middle negative layer and an upper positive layer.
鶴見 美和*; 榎戸 輝掲*; 一方井 祐子*; Wu, T.*; Wang, D.*; 篠田 太郎*; 中澤 知洋*; 辻 直樹*; Diniz, G.*; 片岡 淳*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 50(13), p.e2023GL103612_1 - e2023GL103612_9, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Gamma-ray glows are observational evidence of relativistic electron acceleration due to the electric field in thunderclouds. However, it is yet to be understood whether such relativistic electrons contribute to the initiation of lightning discharges. To tackle this question, we started the citizen science "Thundercloud Project," where we map radiation measurements of glows from winter thunderclouds along Japan's sea coast area. We developed and deployed 58 compact gamma-ray monitors at the end of 2021. On 30 December 2021, five monitors simultaneously detected a glow with its radiation distribution horizontally extending for 2 km. The glow terminated coinciding with a lightning flash at 04:08:34 JST, which was recorded by the two radio-band lightning mapping systems, FALMA and DALMA. The initial discharges during the preliminary breakdown started above the glow, that is, in vicinity of the electron acceleration site. This result provides one example of possible connections between electron acceleration and lightning initiation.
雨森 道紘*; 土屋 晴文; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 他111名*
Collaboration*; 他111名*
Physical Review Letters, 127(3), p.031102_1 - 031102_6, 2021/07
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:87.51(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report observations of gamma-ray emissions with energies in the 100-TeV energy region from the Cygnus region in our Galaxy. Two sources are significantly detected in the directions of the Cygnus OB1 and OB2 associations. Based on their positional coincidences, we associate one with a pulsar PSR J2032 + 4127 and the other mainly with a pulsar wind nebula PWN G75.2 + 0.1, with the pulsar moving away from its original birthplace situated around the centroid of the observed gamma-ray emission. This work would stimulate further studies of particle acceleration mechanisms at these gamma-ray sources.
雨森 道紘*; 土屋 晴文; Tibet AS Collaboration*; 他93名*
Collaboration*; 他93名*
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(5), p.460 - 464, 2021/05
被引用回数:64 パーセンタイル:98.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Cosmic rays (protons and other atomic nuclei) are believed to gain energies of petaelectronvolts (PeV) and beyond at astrophysical particle accelerators called "PeVatrons" inside our Galaxy. Although a characteristic feature of a PeVatron is expected to be a hard gamma-ray energy spectrum that extends beyond 100 teraelectronvolts (TeV) without a cut-off, none of the currently known sources exhibit such a spectrum owing to the low maximum energy of accelerated cosmic rays or owing to insufficient detector sensitivity around 100 TeV. Here, we report the observation of gamma-ray emission from the supernova remnant G106.3+2.7 above 10 TeV. This work provides flux data points up to and above 100 TeV and indicates that the very-high-energy gamma-ray emission above 10 TeV is well correlated with a molecular cloud rather than with the pulsar PSR J2229+6114. Regarding the gamma-ray emission mechanism of G106.3+2.7, this morphological feature appears to favour a hadronic origin via the 
 decay caused by accelerated relativistic protons over a leptonic origin via the inverse Compton scattering by relativistic electrons. Furthermore, we point out that an X-ray flux upper limit on the synchrotron spectrum would provide important information to firmly establish the hadronic scenario as the mechanism of particle acceleration at the source.
decay caused by accelerated relativistic protons over a leptonic origin via the inverse Compton scattering by relativistic electrons. Furthermore, we point out that an X-ray flux upper limit on the synchrotron spectrum would provide important information to firmly establish the hadronic scenario as the mechanism of particle acceleration at the source.
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 久保 守*; 中澤 知洋*; 篠田 太郎*; 米徳 大輔*; 澤野 達哉*; 湯浅 孝行*; 牛尾 知雄*; 佐藤 陽祐*; et al.
Geophysical Research Letters, 48(7), 11 Pages, 2021/04
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:90.11(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)graupels
雨森 道紘*; 土屋 晴文; Tibet AS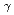 Collaboration*; 他93名*
Collaboration*; 他93名*
Physical Review Letters, 126(14), p.141101_1 - 141101_7, 2021/04
被引用回数:112 パーセンタイル:99.57(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report, for the first time, the long-awaited detection of diffuse gamma rays with energies between 100 TeV and 1 PeV in the Galactic disk. Particularly, all gamma rays above 398 TeV are observed apart from known TeV gamma-ray sources and compatible with expectations from the hadronic emission scenario in which gamma rays originate from the decay of 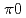 's produced through the interaction of protons with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy. This is strong evidence that cosmic rays are accelerated beyond PeV energies in our Galaxy and spread over the Galactic disk.
's produced through the interaction of protons with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy. This is strong evidence that cosmic rays are accelerated beyond PeV energies in our Galaxy and spread over the Galactic disk.
湯浅 孝行*; 和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 古田 禄大; 土屋 晴文; 久富 章平*; 辻 結菜*; 奥田 和史*; 松元 崇弘*; 中澤 知洋*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2020(10), p.103H01_1 - 103H01_27, 2020/10
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:74.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We designed, developed, and deployed a distributed sensor network aiming at observing high-energy ionizing radiation, primarily gamma rays, from winter thunderclouds and lightning in coastal areas of Japan. Starting in 2015, we have installed, in total, more than 15 units of ground-based detector system in Ishikawa Prefecture and Niigata Prefecture, and accumulated 551 days of observation time in four winter seasons from late 2015 to early 2019. In this period, our system recorded 51 gamma-ray radiation events from thundercloud and lightning. Highlights of science results obtained from this unprecedented amount of data include the discovery of photonuclear reaction in lightning which produces neutrons and positrons along with gamma rays, and deeper insights into the life cycle of a particle-acceleration and gamma-ray-emitting region in a thunder-cloud. The present paper reviews objective, methodology, and results of our experiment, with a stress on its instrumentation.
和田 有希*; 榎戸 輝揚*; 中村 佳敬*; 森本 健志*; 佐藤 光輝*; 牛尾 知雄*; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 米徳 大輔*; 澤野 達也*; et al.
Journal of Geophysical Research; Atmospheres, 125(4), p.e2019JD031730_1 - e2019JD031730_11, 2020/02
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:80.58(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)During 2017-2018 winter operation of the Gamma-Ray Observation of Winter Thunderclouds experiment in Japan, two downward terrestrial gamma-ray flashes (TGFs) that triggered atmospheric photonuclear reactions were detected. They took place during winter thunderstorms on 5 December 2017 and 9 January 2018 at Kanazawa, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. Each event coincided with an intracloud/intercloud discharge, which had a negative-polarity peak current higher than 150 kA. Their radio waveforms in the low-frequency band are categorized as a distinct lightning type called energetic in-cloud pulse (EIP). Negative-polarity EIPs have been previously suggested to be highly associated with downward TGFs, and the present observations provide evidence of the correlation between them for the first time. Furthermore, both of the downward TGFs followed gamma-ray glows, minute-lasting high-energy emissions from thunderclouds. It is suggested that the negative EIPs took place with downward propagating negative leaders or upward positive ones developed in highly electrified regions responsible for the gamma-ray glows.
冠城 雅晃; 鳥居 建男; 小川 徹
JAEA-Review 2019-031, 251 Pages, 2020/01
福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉をはじめとした過酷な放射線環境下で、現場作業者の被ばく線量を低減するため、遠隔技術やロボティクスの高度化に大きな期待が集まっている。しかし、ロボットの遠隔制御のための最先端の要素技術やセンサー, 電子機器の耐放射線性にも厳しい限界がある。原子力へのロボット技術の応用拡大に向けて、機器の耐放射線性の向上(Radiation hardness)や運用における放射線環境への適応力(Radiation smartness)が求められる。さらに、将来の核燃料デブリの探査と取り出しに向けては、福島第一原子力発電所内の高線量率現場での放射線イメージングや核燃料デブリの検出といった、放射線計測(Radiation measurement)および位置認識・周辺環境の把握のための技術の開発が必要である。今回の福島リサーチカンファレンスでは、遠隔技術のさらなる進展のため、さまざまな分野の専門化を交えて将来のビジョンを共有することを目指している。
若井田 育夫; 長谷川 秀一*; 田所 孝広*
日本機械学会誌, 122(1211), p.18 - 20, 2019/10
廃炉国際ワークショップ(FDR 2019) Track4での議論について概説した。放射線計測分野では、耐放射線性を意識した検出素子・検出機器開発、プラントモニタリングへの適用、そして廃炉作業現場で、まず最初に不可欠となる放射線源(汚染源)の可視化(イメージング)技術に関する議論が展開された。検出素子や周辺機器の耐放射線性が確実に進展していること、可視化技術が実用レベルにある状況が報告される一方、その基本が単一フォトン検出手法の領域にあり、高放射線場における高カウントレート核種同定の困難さが改めて認識された。今後の重要課題といえる。レーザー利用計測分野については、特定元素・同位体の選択的共鳴励起・イオン化による質量分析手法の高度化技術と、遠隔その場分析を可能とするLaser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy(LIBS)等の発光分光技術に関する議論等が展開された。新奇で革新的な手法への挑戦よりも、これまで構築してきた手法を基本とし、その確実性に着眼する方向性が見られ、レーザー分析で重要となる光源の改善検討も含め、実現に向けた取り組みが問われていることが理解できる。
高橋 史明
原子力のいまと明日, p.109 - 111, 2019/03
日本原子力学会では、一般向けの解説として、「原子力のいまと明日-東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故の経験から」の出版を企図した。この解説書では、原子力発電所の概要、東京電力福島第一原子力発電所事故やその後の対応等とともに、放射線の基礎知識や利用についても解説を与える。本稿では、放射線計測や防護で用いられる単位として、基本となる吸収線量などの物理量、放射線防護の目的で用いられる防護量及び計測のために定義される実用量を解説する。また、放射線作業環境で実測され、内部被ばく防護の基本となる放射能の単位についても説明する。さらに放射線管理の現場で有用な単位として、放射能と線量を関係づける線量率定数を紹介する。
吉本 政弘; Saha, P. K.; 加藤 新一; 岡部 晃大; 山本 風海; 金正 倫計
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1048 - 1050, 2018/06
J-PARC 3GeVシンクロトロン加速器(RCS)では1MWの大強度陽子ビームを実現するために、荷電変換ビーム多重入射方式を採用している。従来のセプタム・バンプ電磁石のみを使ったビーム多重入射方式に比べてセプタム境界面でのビーム損失はほとんど起こらないため、原理的には多重入射する回数に制限は存在しない。しかし、詳細な残留線量測定の結果、荷電変換フォイルの周辺に非常に強い残留線量があることが分かった。PHITSシミュレーションの結果は、この強い放射化の原因が荷電変換方式ビーム多重入射時に、入射ビーム及び周回ビームが荷電変換フォイルに衝突することで起こる核反応による2次粒子によって引き起こされていることを強く示唆していた。このことを明らかにするために、フォイルからの2次粒子計測が重要になってくる。そこで、100度ダンプラインに新たにフォイル導入装置を設置し、2次粒子計測に必要な単純な実験系を構築した。ここでは、2次粒子の直接計測と金属薄膜を用いた放射化法による計測の2種類を計画している。まずは放射化法についてPHITSコードを用いた検討を開始した。銅サンプルにエネルギーの異なる陽子または中性子を照射した際に生成される核種の内、 線放出核種を選択し、陽子もしくは中性子に選択的に反応する標的を探した。その結果、
線放出核種を選択し、陽子もしくは中性子に選択的に反応する標的を探した。その結果、 Zn及び
Zn及び Coが陽子の標的として、
Coが陽子の標的として、 Coが中性子の要的として使えることが分かった。
Coが中性子の要的として使えることが分かった。
吉本 政弘; 原田 寛之; 加藤 新一; 金正 倫計; 岡部 晃大
Proceedings of 6th International Beam Instrumentation Conference (IBIC 2017) (Internet), p.461 - 465, 2018/03
J-PARC RCSでは、1MWの大強度陽子ビーム運転を実現するためにビームロスの抑制と制御に多大なる努力を費やしてきた。我々の主要ビームロスモニタはセル毎の広い範囲でのビームロスを検出することを主眼に置いていたため、ビームロスに関する詳細なメカニズムを調査するには不十分であった。そこで、ビームロススポットを検出しかつ電磁石の中でも使える新式のシンチレーション型ビームロスモニタを導入した。この新式ビームロスモニタは小型シンチレータと光電子増倍管を分離し、光ファイバーで接続する構成になっている。小型シンチレータを真空ダクトに直接接触させているため、ロススポットに対して感度を高めることが可能となった。一方、光電子増倍管を分離して電磁石から遠ざけることができたため、動磁場による増幅率への影響を防ぐことが可能となった。この新式ビームロスモニタの導入により、1MW大強度ビーム運転を安定的に行うことが可能となる。本発表では、この新式ビームロスモニタについて詳細に発表する。
 -ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter
-ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter越智 康太郎; 佐々木 美雪; 石田 睦司*; 濱本 昌一郎*; 西村 拓*; 眞田 幸尚
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8), p.926_1 - 926_14, 2017/08
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:22.71(Environmental Sciences)福島第一原子力発電所事故後、環境中の放射性セシウムの挙動を把握するために土壌中放射性セシウムの深度分布が調査されてきた。一般的な放射性セシウムの深度分布の測定手法は、土壌試料の採取及び放射能測定といった観点から煩雑である。本研究では、我々は無人ヘリコプターを用いた上空からの放射線計測により得られた 線スペクトルの特徴に着目することで、放射性セシウムの深度分布の推定手法を確立した。本手法は、放射性セシウムの深度分布を定量的に評価するために、様々な深さにおける散乱
線スペクトルの特徴に着目することで、放射性セシウムの深度分布の推定手法を確立した。本手法は、放射性セシウムの深度分布を定量的に評価するために、様々な深さにおける散乱 線に対する直接
線に対する直接 線の比の変動に着目した。結果から、前述の遠隔測定の結果と実際の土壌中放射性セシウムの深度分布との間に正の相関があることが分かった。
線の比の変動に着目した。結果から、前述の遠隔測定の結果と実際の土壌中放射性セシウムの深度分布との間に正の相関があることが分かった。
三枝 純; 田川 明広; 操上 広志; 飯島 和毅; 吉川 英樹; 時澤 孝之; 中山 真一; 石田 順一郎
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 3(3), p.15-00609_1 - 15-00609_7, 2016/06
福島第一原子力発電所の事故後、原子力機構は福島県内の学校施設を効果的に除染するための方法を構築するため各種の除染実証試験((1)校庭の線量低減対策、(2)遊泳用プール水の浄化、(3)遊具表面の除染)を実施した。これらの除染実証試験を通して、(1)校庭の線量低減対策では、校庭の表土を剥ぎ取り深さ1mのトレンチに埋設することで線量を大幅に低減できること、(2)遊泳用プール水の浄化では、水中の放射性セシウムを回収するために凝集沈殿法が有効であること、(3)遊具表面の除染では、鉄棒や砂場の木枠といった遊具に対する除染効果は遊具の材質や塗装の条件により大きく依存すること、等の知見を得た。本稿では、これらの除染実証試験についてレビューする。
三枝 純; 田川 明広; 操上 広志; 飯島 和毅; 吉川 英樹; 時澤 孝之; 中山 真一; 石田 順一郎
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
福島第一原子力発電所の事故後、原子力機構は福島県内の学校施設を効果的に除染するための方法を構築するため各種の除染実証試験((1)校庭の線量低減対策、(2)遊泳用プール水の浄化、(3)遊具表面の除染)を実施した。これらの除染実証試験を通して、(1)校庭の線量低減対策では、校庭の表土を剥ぎ取り深さ1mのトレンチに埋設することで線量を大幅に低減できること、(2)遊泳用プール水の浄化では、水中の放射性セシウムを回収するために凝集沈殿法が有効であること、(3)遊具表面の除染では、鉄棒や砂場の木枠といった遊具に対する除染効果は遊具の材質や塗装の条件により大きく依存すること、等の知見を得た。本稿では、これらの除染実証試験についてレビューする。
西谷 健夫
放射線, 31(2), p.97 - 104, 2005/04
トカマクを中心とするプラズマの磁場閉じ込めの研究では、核融合の科学的実証を目指して研究が進められており、すでに米国のTFTRとEUのJETではDTプラズマ実験が実施された。また現在国際熱核融合実験炉ITERの設計が国際協力で進められており、まさにその建設が決まろうとしている。核反応を伴わないプラズマの診断では、プラズマから放出される電磁波や中性粒子が主な測定対象になっていたが、DD反応やDT反応などの核反応を伴うプラズマでは、中性子, 粒子を初めとする高速荷電粒子,
粒子を初めとする高速荷電粒子, 線といった放射線が大量に放出され、それらの計測はプラズマ診断の大きな手段になってきている。ここではITERにおける核燃焼プラズマの計測を中心に放射線を用いたプラズマ診断について紹介する。
線といった放射線が大量に放出され、それらの計測はプラズマ診断の大きな手段になってきている。ここではITERにおける核燃焼プラズマの計測を中心に放射線を用いたプラズマ診断について紹介する。
生田 優子; 蔀 肇*; 佐伯 正克
日本原子力学会誌, 44(10), p.744 - 745, 2002/10
国際原子力総合技術センターが文科省から受託している「国際原子力安全技術研修事業」で実施している、指導教官研修と講師海外派遣研修について、その概要を纏めたものである。
量子計測研究グループ
JAERI-Conf 98-011, 84 Pages, 1998/07
21世紀における放射線計測を考えると、量子現象を利用した新しい放射線検出原理を追及することが研究者にとって1つの大きな課題・目標となる。このような状況の中で量子計測研究グループでは、平成5年4月から5年間「量子計測法の研究」テーマのもとで、He-Neレーザー等を用いた中性子検出法の研究、耐放射線性光ファイバーの開発研究及び超伝導トンネル接合放射線検出器の研究の3つの研究を行った。これらの研究を終了するに当たり1998年1月19,20日に「量子計測法の研究」と題する研究会を開催した。本稿は同研究会での講演内容を論文等としてまとめたもので、所内外で精力的に行われている先端的な研究の現状を知ると共に、将来における「量子現象を利用した放射線計測法」の方向と展開を知る上で多くの示唆に富む内容を含むものである。